Gum Grafting Procedures
(Subepithelial Connective Tissue Grafts)
When recession of the gingiva occurs, the body loses a natural defense against both bacterial penetration and trauma. When gum recession is a proble, gum reconstruction using grafting techniques is an option.
When there is only minor recession, some healthy gingiva often remains and protects the tooth, so that no treatment other than modifying home care practices is necessary. However, when recession reaches the mucosa, the first line of defense against bacterial penetration is lost.
In addition, gum recession often results in root sensitivity to hot and cold foods as well as an unsightly appearance of the gum and tooth. When significant, gum recession can predispose to worsening recession and expose the root surface, which is softer than enamel, leading to root caries and root gouging.
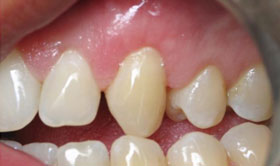
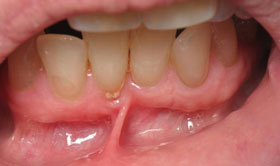
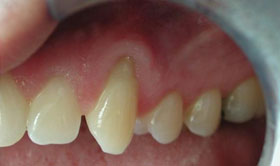
A gingival graft is designed to solve these problems. A thin piece of tissue is taken from the roof of the mouth or gently moved over from adjacent areas to provide a stable band of attached gingiva around the tooth. The gingival graft may be placed in such a way as to cover the exposed portion of the root.
The gingival graft procedure is highly predictable and results in a stable healthy band of attached tissue around the tooth.
Free Gingival graft
A gingival graft is designed to limit recession by providing a stable band of attached gingiva or gum tissue around the tooth. This soft tissue barrier prevents further recession and infection.
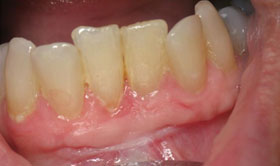
Connective Tissue Graft
Exposed tooth roots are the result of gum recession. Gum recession often results in root sensitivity to hot and cold foods as well as an unsightly appearance of the gum and tooth. A connective tissue graft will help by covering one or more of these roots that make your teeth appear too long.